Describe the Different Means of Locomotion Used by Prokaryotes
Hence the movement in protozoan includes. Protist locomotion describes the different modes of movement that the eukaryotic organisms utilize.
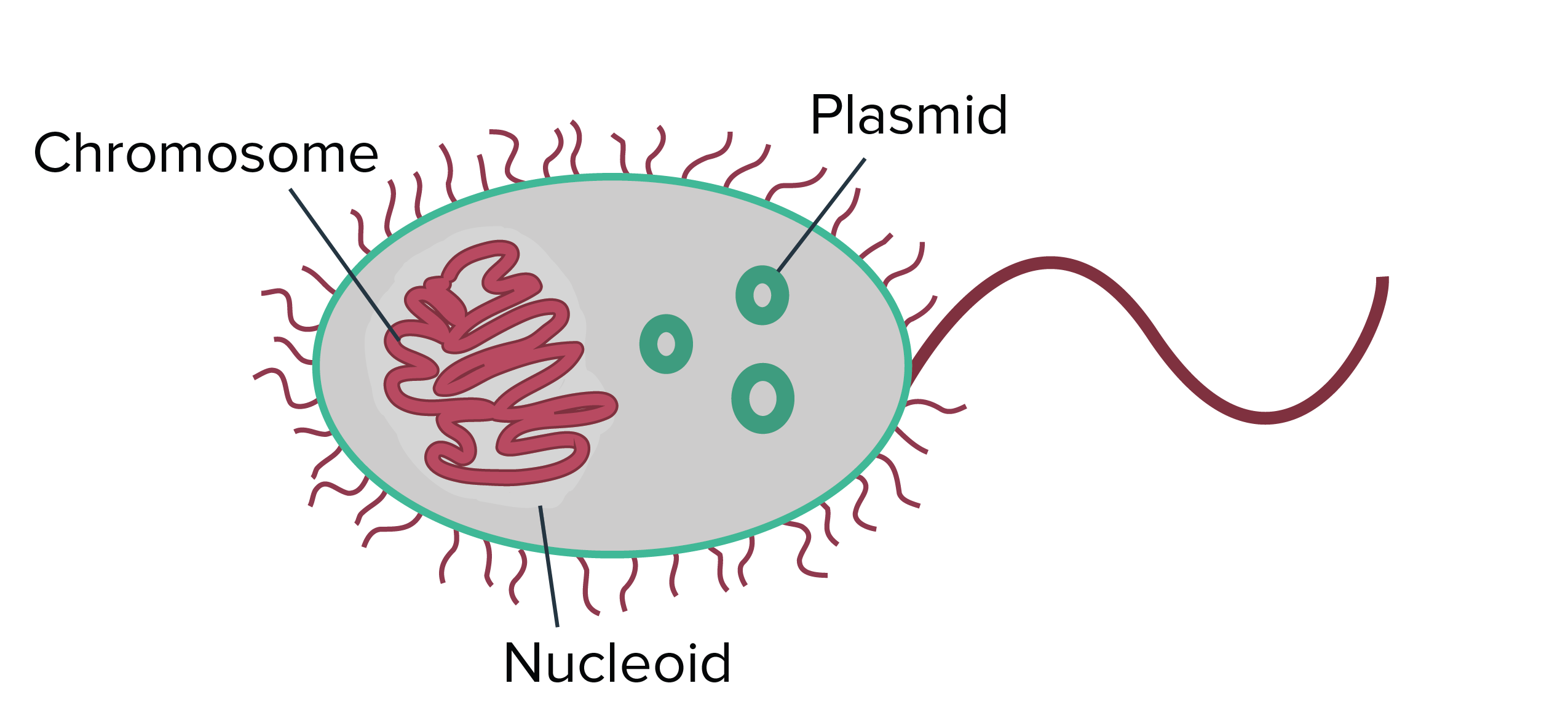
Prokaryote Structure Article Khan Academy
3 runswim means the its motility is in one direction for a length of time running toward something its a positive stimulus there are few tumbles 4 when its counterclockwise the flagella will tumble 5 tumble means youre running away from.
. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have them but theyre more complex in eukaryotes. Cilia and flagella are also known among plants and animals although they are totally absent from the true fungi. Locomotion is the type of movement you use when performing an action to put it in lay terms.
Discover the three main methods of transportation protists utilize including cilia flagellates. Some prokaryotes have flagella pili or fimbriae. A flagellum plural flagella is a long appendage specialized for locomotion and while both eukaryotes and prokaryotes may exhibit flagellar motion the flagella of prokaryotes are quite different structurally from those of eukaryotes.
The following points highlight the five modes of locomotion in Protists. To help with locomotion flagella are present though pilus can also serve as an aid for locomotion. Ciliary movement flagellar movement and amoeboid movement.
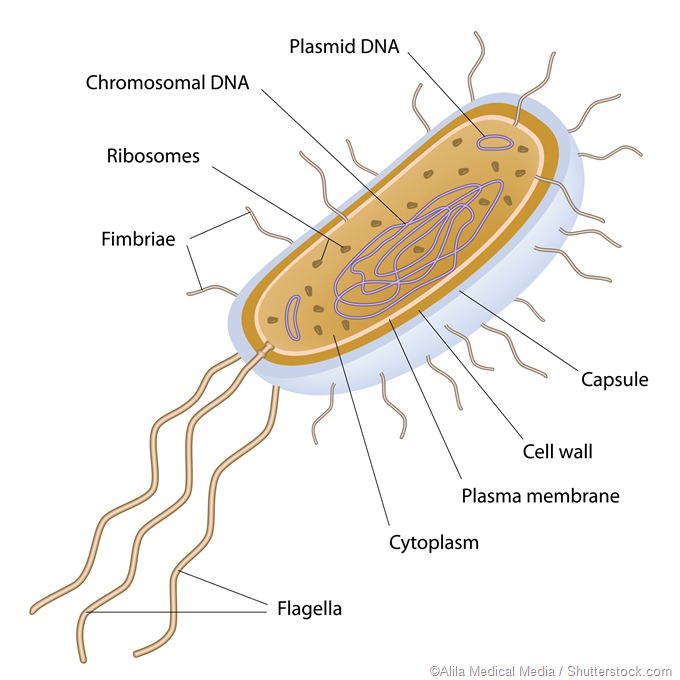
Explain the different means by which bacterial cells are able to move. In eukaryotic cells they move in a wave motion and propel the cells more slowly. Most prokaryotes also contain plasmids which contains small circular pieces of DNA.
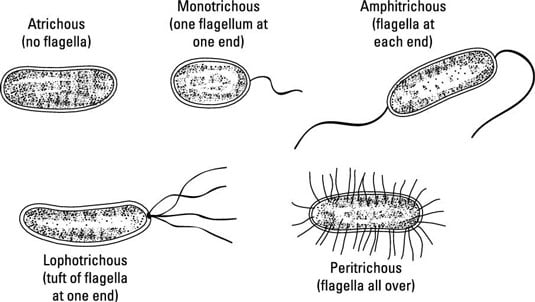
-Long helical structures -Composed of the protein flagellin-Involved in locomotion. Movement can involve surface appendages such as flagella that spin pili that pull and Mycoplasma legs that walk. The different kinds of flagellar arrangement on bacterial cells are shown here.
What are two cell structures that can be used for locomotion. Those organelles give their names to informal groupsflagellates and ciliatesof protists A lesser number of. Those eukaryotic organelles are.
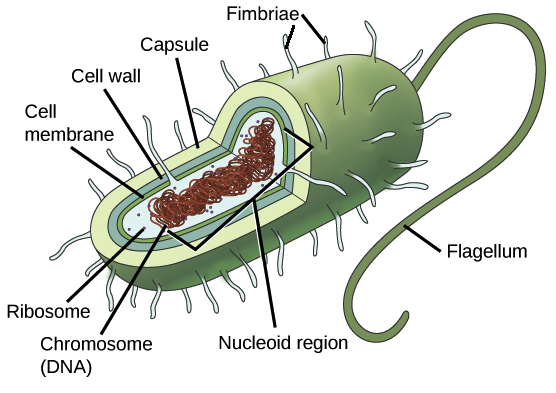
The organs for locomotion are cilia and flagella. Flagella are used for locomotion while most pili are used to exchange genetic material during a type of reproduction called conjugation. In prokaryotic cells flagella spin around and propel the cells very quickly.
The most common type of movement in prokaryotes is through flagellar action. Prokaryotic flagella consist of tightly wound. Prokaryotic cells move through liquids or over moist surfaces by swimming swarming gliding twitching or floating.
Describe strategies employed by prokaryotes to exchange genetic information and survive non- permissive conditions. Thus in different prokaryotes locomotion vary which depends upon the presence of these locomotary organs. Describe the different ways that prokaryotes acquire energy and.
Locomotion by Mucilage Propulsion. The motions made by flagella are smooth and wave-like among eukaryotes. Common examples of Prokaryotic organisms are bacteria and archaea.
What locomotion do you use when you sprint. Protozoa are eukaryotic organism having specialized organs for locomotion. The cell wall acts as an extra layer of protection helps the cell maintain its shape and prevents dehydration.
Humans use plantigrade locomotion for walking running. Many prokaryotes also have a cell wall and capsule. An impressive diversity of motility mechanisms has evolved in prokaryotes.
A few forms can move by gliding or floating although the vast majority move by means of whips or small hairs known as flagella or cilia respectively. Prokaryotes on the other hand whip their flagella like a rotating propeller. Also all members of Kingdom Monera are prokaryotes.
0 Response to "Describe the Different Means of Locomotion Used by Prokaryotes"
Post a Comment